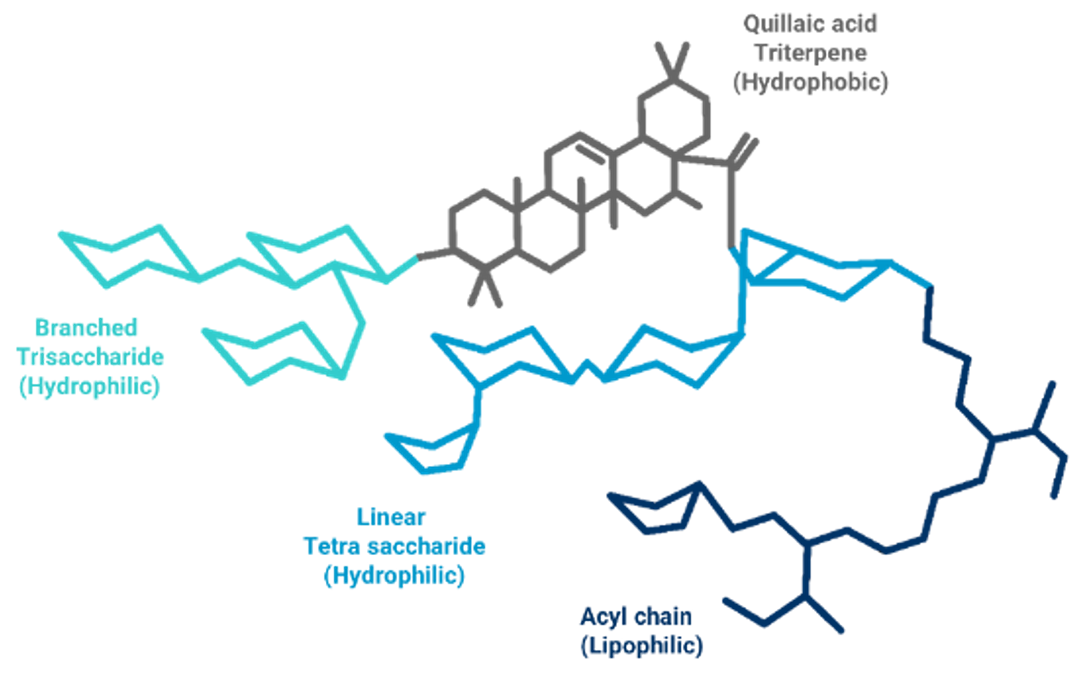
Quillaja saponins, generally extracted from Quillaja saponaria tree, are considered non-ionic, high molecular weight complex glycosides known for their diverse biological and surfactant activities.
A saponin molecule is composed of a triterpenoid aglycone lipophilic moiety and sugars (glucose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, arabinose, and xylose) as the hydrophilic moiety. The aldehyde group attached to the core aglycone binds to the free amino groups of Antigen Presenting Cells. Acyl elements of the saponin molecule can enhance the activation of CTL against exogenous antigens. The sugar chain is essential for initiating the immune-activating mechanism. The balance between these hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties is crucial for maintaining the adjuvanticity of saponins.